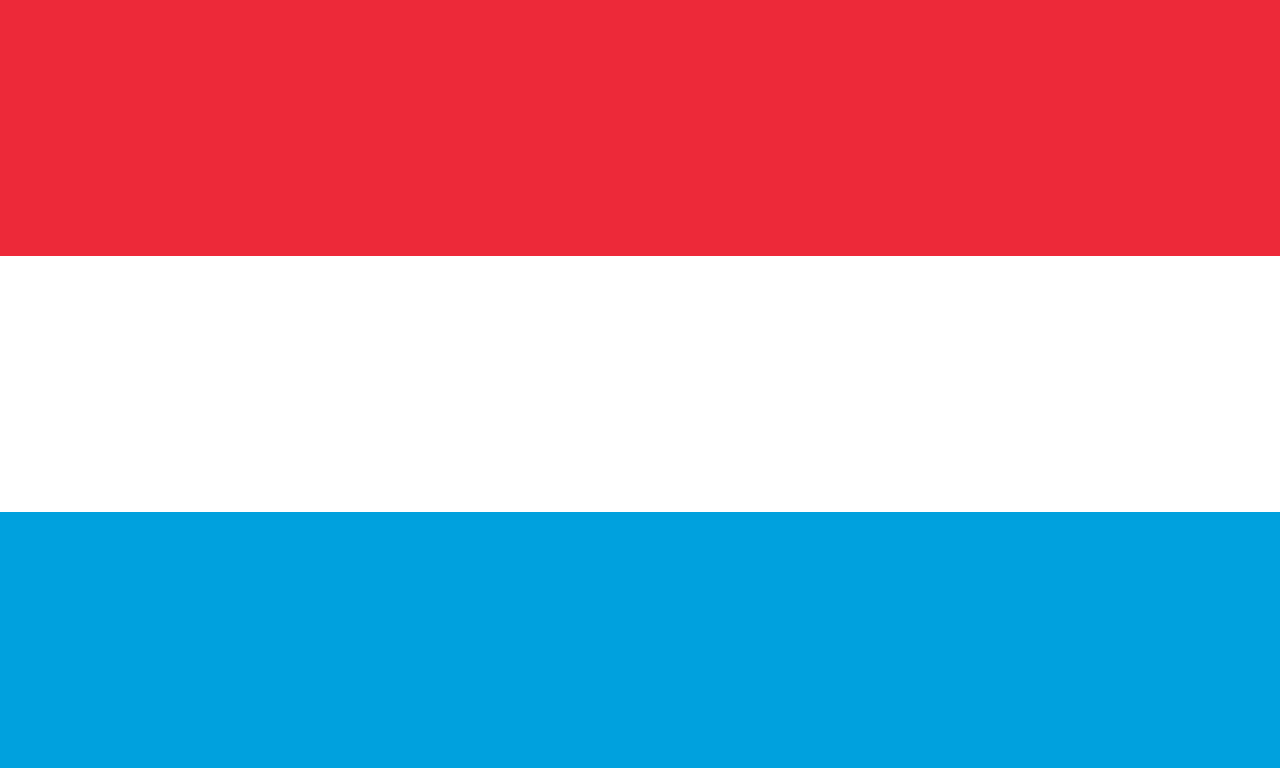
The flag of Liechtenstein consists of two horizontal stripes of blue (top) and red (bottom), with a gold crown in the upper hoist-side corner. This simple yet distinctive design encapsulates Liechtenstein's rich history, cultural heritage, and unique status as a principality.
Liechtenstein information
| National Flag Day | — |
| Sovereign state | Yes |
| Official name | Principality of Liechtenstein |
| Capital | Vaduz |
| Population | 38,114 |
| Area | 160 km² |
| Currency | Swiss franc (CHF) |
| Language | German, Alemannic |
| Continent | Europe |
| Region | Western Europe |
| Subregion | Alpine countries |
| Borders | Austria, Switzerland |
| Timezone | Central European Time (CET) UTC+1 |
| Calling code | +423 |
| Top-level domain | .li |
History of the Liechtenstein flag
 The current version of the Liechtenstein flag was officially adopted on June 30, 1982. However, its basic design dates back to 1764, when Prince Joseph Wenzel I introduced the blue and red colors as the principality's livery colors. The gold crown was added to the flag in 1937 by Prince Franz Joseph II to distinguish it from the flag of Haiti, which was identical at the time. This addition came after the 1936 Berlin Olympics, where it was discovered that the two countries had the same flag. The 1982 adoption formalized the flag's design and proportions, ensuring its consistent use as a national symbol.
The current version of the Liechtenstein flag was officially adopted on June 30, 1982. However, its basic design dates back to 1764, when Prince Joseph Wenzel I introduced the blue and red colors as the principality's livery colors. The gold crown was added to the flag in 1937 by Prince Franz Joseph II to distinguish it from the flag of Haiti, which was identical at the time. This addition came after the 1936 Berlin Olympics, where it was discovered that the two countries had the same flag. The 1982 adoption formalized the flag's design and proportions, ensuring its consistent use as a national symbol.
Symbolism and design of the Liechtenstein flag
Each element of the Liechtenstein flag carries symbolic meaning. The blue stripe represents the sky and the country's position high in the Alps. It also symbolizes the peace and serenity that characterize this small principality. The red stripe represents the warm evening fires that historically lit up the mountains, serving as beacons for communication across the valleys. Red also symbolizes the warmth and hospitality of the Liechtenstein people. The gold crown in the upper left corner is a powerful symbol of the principality's monarchy and its constitutional system. It represents the unity between the Prince of Liechtenstein and the country's citizens, emphasizing the balance between monarchical tradition and democratic principles that defines Liechtenstein's governance.
Usage and significance of the Liechtenstein flag
 The flag of Liechtenstein is a source of national pride and is prominently displayed throughout the country. It flies on government buildings, schools, and during national celebrations such as National Day (August 15). The flag plays a crucial role in fostering unity and identity among Liechtenstein's small population of about 38,000 people. In international contexts, the flag represents Liechtenstein in diplomatic settings, sports events, and cultural exchanges, symbolizing the country's sovereignty and unique position as one of the world's smallest nations. During times of national significance, the flag serves as a rallying point for Liechtensteiners, embodying their shared heritage and commitment to their country's values.
The flag of Liechtenstein is a source of national pride and is prominently displayed throughout the country. It flies on government buildings, schools, and during national celebrations such as National Day (August 15). The flag plays a crucial role in fostering unity and identity among Liechtenstein's small population of about 38,000 people. In international contexts, the flag represents Liechtenstein in diplomatic settings, sports events, and cultural exchanges, symbolizing the country's sovereignty and unique position as one of the world's smallest nations. During times of national significance, the flag serves as a rallying point for Liechtensteiners, embodying their shared heritage and commitment to their country's values.
Interesting facts about the Liechtenstein flag
- Liechtenstein is one of the few countries to have added an element to its flag (the crown) specifically to differentiate it from another nation's flag.
- The flag's colors of blue and red are also featured prominently in the coat of arms of the Princely House of Liechtenstein, emphasizing the close connection between the monarchy and the state.
- Despite being one of the world's smallest countries, Liechtenstein has a thriving economy and is known for its financial services sector, a fact reflected in the stability and continuity symbolized by its flag.
- The proportions of the Liechtenstein flag are 3:5, which is relatively uncommon among national flags.
- On National Day, it's customary for Liechtenstein citizens to display the national flag outside their homes, creating a sea of blue and red across the country.